What Causes Hormonal Imbalance?
Hormonal imbalances occur when there’s either too much or too little of a hormone in your body. Since hormones control nearly every function — from your mood and metabolism to reproductive health and energy levels — even a small imbalance can have a big impact. For example, too much cortisol (the stress hormone) can leave you feeling anxious and exhausted, while low thyroid hormones can slow down your metabolism and leave you feeling sluggish.
The good news? You can take natural steps to restore balance and feel like yourself again!

Key Hormones That Shift as Women Age
As women age, hormone levels naturally fluctuate. Some key hormones that can get out of balance include:
Estrogen & Progesterone
These hormones shift during perimenopause and menopause, leading to symptoms like mood swings, weight gain, and sleep disturbances.
Cortisol (Stress Hormone)
Chronic stress can lead to high cortisol levels, causing fatigue, belly fat storage, and sleep issues.
Insulin
Poor diet, excess sugar, and lack of exercise can make insulin less effective, leading to blood sugar spikes and energy crashes.
Thyroid Hormones
The thyroid regulates metabolism, and imbalances can lead to weight gain, fatigue, and brain fog.
Testosterone
Women need some testosterone for muscle growth and energy, but levels can decline with age.
Melatonin
This sleep hormone can decrease due to stress, poor sleep habits, and screen time before bed.
Check Out Our Hormone Balance Food Chart! Print it out and stick it on your fridge—perfect for your next grocery trip!
Common Causes of Hormonal Imbalance
Hormonal imbalances can arise from various factors, including:
1. Chronic Stress (Affects Cortisol Levels)
Constant stress leads to high cortisol, which can cause fatigue, weight gain, and sleep issues.
2. Poor Diet (Too Much Sugar, Unhealthy Fats, Processed Foods)
A diet high in sugar and processed foods can disrupt insulin and thyroid function, affecting overall hormone balance.
3. Lack of Physical Activity or Over-Exercising
Sedentary habits or excessive exercise can throw off hormones, affecting metabolism and reproductive health.
4. Poor Sleep Quality
Poor sleep, especially from stress or screen time, reduces melatonin and disrupts cortisol and reproductive hormones.
5. Gut Health Issues
An unhealthy gut can lead to inflammation, affecting hormones like estrogen and thyroid hormones, causing issues like bloating or weight gain.
6. Environmental Factors (Toxins, Chemicals in Food and Beauty Products)
Exposure to toxins in food, beauty products, or plastics can interfere with your body’s natural hormones.
7. Aging and Menopause
As women age, fluctuations in estrogen and progesterone during perimenopause and menopause can cause symptoms like mood swings, weight gain, and sleep disturbances.
8. Medical Conditions (Thyroid Disorders, Insulin Resistance)
Conditions like thyroid disorders and insulin resistance can directly impact hormone levels, leading to symptoms like fatigue, weight changes, and difficulty managing blood sugar.
By addressing these common causes, you can work to restore balance and improve overall health.
Symptoms of Hormonal Imbalance
1. Irregular Periods or Intense PMS
Hormonal imbalances, particularly with estrogen and progesterone, can cause periods to become irregular, heavier, or lighter than usual. You might also experience more severe PMS symptoms like bloating, irritability, and breast tenderness.
2. Mood Swings, Anxiety, or Feeling Down
Changes in hormone levels, especially estrogen and progesterone, can affect your brain chemistry, leading to mood swings, anxiety, or even depression. This is common around the time of menopause, perimenopause, or during times of stress.
3. Unexplained Weight Gain or Trouble Losing Weight
Hormones like insulin, thyroid hormones, and cortisol play a role in regulating metabolism. When these hormones are out of balance, it can lead to weight gain or make it harder to lose weight, even with healthy eating and exercise.
4. Feeling Drained or Constantly Fatigued
Low levels of thyroid hormones or cortisol can leave you feeling tired all the time, even after a full night’s sleep. This kind of fatigue is more than just feeling sleepy—it’s an ongoing lack of energy that doesn’t seem to go away.
5. Trouble Sleeping (Insomnia or Night Sweats)
Hormones like melatonin, estrogen, and progesterone are crucial for sleep regulation. Low levels of these hormones, especially during menopause or stress, can lead to insomnia, frequent waking during the night, or even night sweats.
6. Digestive Issues, Bloating, and Gut Discomfort
Hormonal imbalances, particularly with estrogen and cortisol, can affect your digestive system. This might lead to bloating, constipation, diarrhea, or even food sensitivities. A disrupted gut microbiome can also worsen these symptoms.
7. Skin Problems (Acne, Dryness, or Increased Sensitivity)
Fluctuating hormone levels, particularly androgens like testosterone, can trigger acne breakouts, especially in the chin or jawline area. On the flip side, a lack of estrogen can cause dry, sensitive skin, or make existing skin conditions worse.
8. Low Libido or Vaginal Dryness
Estrogen and testosterone are key to sexual health and libido. Hormonal changes, especially as women age, can result in a reduced sex drive or vaginal dryness, making intimacy uncomfortable.
9. Brain Fog or Difficulty Focusing
Imbalanced hormones, particularly estrogen and thyroid hormones, can affect cognitive function. This might show up as brain fog, trouble concentrating, memory lapses, or feeling mentally "cloudy" throughout the day.
These symptoms can be a sign that your hormones need some attention! If you're experiencing several of these, it might be time to look into natural ways to bring your hormones back into balance.

12 Best Ways to Balance Hormones Naturally
1. Eat a Nutrient-Dense, Hormone-Balancing Diet
Why: Your food choices influence your hormonal health by providing the nutrients needed for hormone regulation.
What to do: Focus on whole, unprocessed foods that are rich in healthy fats, fiber, and lean proteins. These foods help stabilize your hormones and support overall health.
- Healthy fats: Avocados, olive oil, nuts, and fatty fish
- High-fiber foods: Cruciferous vegetables, whole grains, chia seeds
- Complete proteins: Grass-fed beef, eggs, lentils, wild-caught salmon
- Blood sugar-balancing foods: Quinoa, brown rice, legumes
Check Out Our Hormone Balance Food Chart! Print it out and stick it on your fridge—perfect for your next grocery trip!
2. Manage Stress and Lower Cortisol Levels
Why: Chronic stress leads to elevated cortisol, which disrupts your hormonal balance.
What to do: Engage in stress-reducing activities to bring your cortisol levels down.
- Try deep breathing, meditation, and yoga
- Incorporate journaling or gratitude practice
- Limit screen time and reduce digital overload
3. Prioritize Sleep for Better Hormonal Health
Why: Adequate, high-quality sleep is essential for hormone production, recovery, and overall health.
What to do: Create a bedtime routine that promotes restful sleep.
- Aim for 7-9 hours of sleep each night
- Reduce blue light exposure before bed
- Try magnesium supplements or chamomile tea to help relax
4. Support Gut Health for Hormone Balance
Why: A healthy gut microbiome helps your body metabolize and detoxify excess hormones.
What to do: Consume foods that promote gut health and improve digestion.
- Fermented foods: Sauerkraut, kimchi, kefir, Greek yogurt
- Fiber-rich foods: Vegetables, fruits, whole grains
- Prebiotic and probiotic-rich foods to support gut health
5. Reduce Sugar and Processed Foods
Why: Refined sugars and processed foods can spike insulin levels, leading to insulin resistance and hormone imbalances.
What to do: Opt for healthier alternatives to satisfy your sweet cravings.
- Dark chocolate
- Nuts and seeds
- Berries with Greek yogurt
- Protein smoothies with healthy fats
6. Strength Training and Regular Exercise
Why: Regular exercise, especially strength training, helps improve metabolism, build muscle mass, and regulate reproductive hormones.
What to do: Incorporate physical activity into your routine.
- Try dumbbell workouts or resistance band exercises
- Engage in walking or light cardio
- Focus on strength training to build muscle
7. Optimize Vitamin D Levels
Why: Vitamin D is critical for hormone regulation, immune function, and overall health.
What to do: Get adequate Vitamin D from sunlight and food sources.
- 15-30 minutes of sunlight exposure daily
- Fatty fish, eggs, and fortified foods
- Consider supplements (Vitamin D3 + K2 for better absorption)
8. Balance Blood Sugar to Prevent Insulin Resistance
Why: Stabilizing blood sugar levels helps prevent insulin resistance and balances hormones.
What to do: Include high-fiber, high-protein foods in your diet to regulate blood sugar.
- Leafy greens, flax seeds, chia seeds
- Whole grains and legumes
- Healthy fats like olive oil
9. Avoid Endocrine Disruptors
Why: Toxins in plastics, beauty products, and cleaning supplies can interfere with hormonal function.
What to do: Reduce exposure to harmful chemicals by making healthier product choices.
- Use glass or stainless steel instead of plastic
- Choose organic skincare and non-toxic household products
- Avoid processed foods with artificial additives
10. Stay Hydrated and Drink Herbal Teas
Why: Hydration supports metabolic processes, detoxification, and hormone balance.
What to do: Drink water and herbal teas to support hydration and hormone regulation.
- Water with lemon for liver detox
- Green tea for antioxidants
- Herbal teas like spearmint and ginger for hormone balance and inflammation reduction
- Bone broth for gut health
11. Incorporate Hormone-Balancing Herbs & Supplements
Why: Certain herbs and supplements can support hormonal health and balance.
What to do: Consider incorporating these herbs and supplements into your routine.
- Ashwagandha (reduces cortisol, improves stress response)
- Maca root (supports reproductive hormones and energy)
- Magnesium (relieves PMS symptoms and improves sleep)
- B Vitamins (support metabolism and energy)
- Omega-3 fatty acids (reduce inflammation and support hormone production)
12. Follow a Hormone-Balancing Meal Plan
Why: A well-structured meal plan that includes hormone-supportive foods can help maintain hormonal balance.
What to do: Plan your meals to include nutrient-dense foods that support hormones like estrogen, insulin, cortisol, and thyroid hormones.
- Focus on whole foods and nutrient-dense options that support overall hormone health
Hormone-Balancing Meal Plan
1. Breakfast: Scrambled eggs with avocado & sautéed spinach / Greek yogurt with flaxseeds & berries
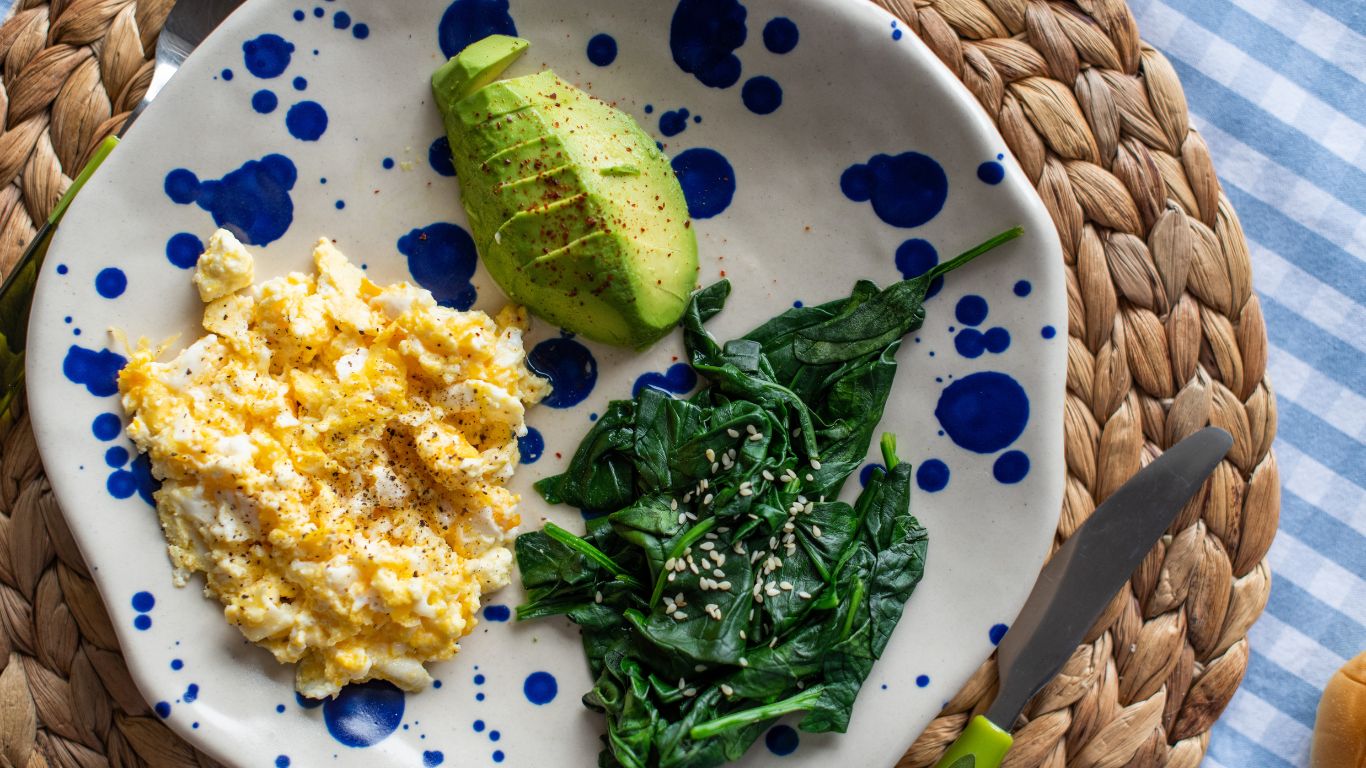

✅ Why it helps:
- Eggs provide high-quality protein and healthy fats, essential for hormone production.
- Avocado is rich in monounsaturated fats, which support estrogen balance and reduce inflammation.
- Spinach is high in magnesium, which helps lower cortisol and improves sleep.
- Greek yogurt contains probiotics, which support gut health and estrogen metabolism.
- Flaxseeds are a great source of lignans, which help balance estrogen levels, especially during perimenopause.
- Berries are packed with antioxidants to reduce inflammation and fight oxidative stress that can mess with hormones.
2. Lunch: Grilled salmon with quinoa & roasted Brussels sprouts / Chickpea salad with olive oil & lemon dressing
.png)
✅ Why it helps:
- Salmon is rich in omega-3 fatty acids, which support brain function, reduce inflammation, and improve insulin sensitivity.
- Quinoa provides fiber and complex carbs, keeping blood sugar levels stable (preventing insulin spikes).
- Brussels sprouts (and other cruciferous veggies) help detox excess estrogen, which is key for hormone balance.
- Chickpeas are high in plant-based protein and fiber, which help regulate insulin and keep you full.
- Olive oil is an excellent source of healthy fats that reduce inflammation and support overall hormone health.
- Lemon helps with digestion and liver detox, which is key for metabolizing hormones properly.
3. Snack: Handful of almonds & dark chocolate / Apple with almond butter
.jpg)
✅ Why it helps:
- Almonds contain healthy fats and vitamin E, which help regulate estrogen levels.
- Dark chocolate (70%+ cacao) is rich in magnesium, which supports cortisol balance and helps with PMS symptoms.
- Apples provide fiber, helping with digestion and blood sugar control.
- Almond butter is full of healthy fats and protein, preventing blood sugar crashes and supporting adrenal health.
4. Dinner: Grass-fed beef or chicken with roasted sweet potatoes & asparagus / Lentil soup with bone broth
.png)
✅ Why it helps:
- Grass-fed beef or chicken provides protein and iron, which are crucial for thyroid function and energy levels.
- Sweet potatoes are a great source of complex carbs, which help reduce stress and support serotonin production (great for sleep and mood!).
- Asparagus is a natural diuretic, helping to eliminate excess estrogen and reduce bloating.
- Lentils are high in fiber and plant-based protein, keeping blood sugar stable.
- Bone broth is rich in collagen, which supports gut health and skin elasticity.
5. Before Bed: Chamomile tea & a handful of walnuts
.png)
✅ Why it helps:
- Chamomile tea reduces cortisol, promotes relaxation, and improves sleep quality.
- Walnuts contain omega-3s and melatonin, which support brain function and regulate sleep cycles.
How This Meal Plan Supports Hormone Balance Overall
✅ Stabilizes Blood Sugar – Reduces insulin spikes that cause energy crashes, weight gain, and mood swings.
✅ Supports Gut Health – Helps the body detox excess estrogen and improves digestion.
✅ Boosts Healthy Fats – Essential for hormone production and reducing inflammation.
✅ Provides Key Vitamins & Minerals – Magnesium, omega-3s, zinc, B vitamins, and antioxidants all play a role in hormone regulation.
✅ Balances Cortisol & Stress Hormones – Foods rich in magnesium, adaptogens, and anti-inflammatory nutrients help lower stress hormones.
By consistently following a meal plan like this, you’ll start to notice improvements in energy levels, mood, metabolism, and overall well-being! 💪✨
Foods to Eat & Avoid for Hormonal Balance
Best Foods for Hormonal Balance:
✅ Fatty fish (salmon, sardines, mackerel)
✅ Cruciferous vegetables (broccoli, kale, cabbage)
✅ Healthy fats (avocado, olive oil, nuts)
✅ Whole grains (quinoa, brown rice, oats)
✅ High-fiber foods (chia seeds, flaxseeds, lentils)
✅ Complete proteins (organic eggs, grass-fed beef, wild-caught fish)
✅ Fermented foods (sauerkraut, kimchi, kefir)
Foods to Avoid:
❌ Refined sugar and processed snacks
❌ Excess caffeine and alcohol
❌ Hydrogenated oils and trans fats
❌ Highly processed foods with artificial additives
Check Out Our Hormone Balance Food Chart! Print it out and stick it on your fridge—perfect for your next grocery trip!
Final Thoughts: Small Changes for Big Results
Balancing hormones naturally is about creating a sustainable, healthy lifestyle. By making small changes in diet, stress management, sleep, and physical activity, women over 35 can support their hormonal health and overall well-being.
Remember, everyone’s hormonal balance is different, so listen to your body and make adjustments that work for you. And if you experience severe symptoms of hormonal imbalance, consult a healthcare provider for personalized medical advice.
References:
Protein Intake and Hormonal Regulation:
Effect of a high-protein diet on ghrelin, growth hormone, and insulin-like growth factor-I:This study discusses how a diet consisting of 30% protein can influence hormones related to appetite and growth. pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov
Strength Training and Muscle Mass in Women Over 35:
Resistance training alters body composition in middle-aged women:This research highlights the effectiveness of resistance training in counteracting age-related muscle mass loss in middle-aged women. pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov
Estrogen's Role in Muscle Health:
Benefits of Estrogen Replacement for Skeletal Muscle Mass and Function:This article explores how estrogen and hormone replacement therapy positively affect muscle mass and function in older females. pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov
Ghrelin and Energy Regulation:
The Physiological Role of Ghrelin in the Regulation of Energy and Glucose Metabolism:This review delves into ghrelin's role in appetite control and energy balance. pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov
Resistance Training and Muscle Strength:
The effect of resistance training programs on lean body mass in postmenopausal women:This study examines how resistance training impacts body composition and muscle strength in postmenopausal women. pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov
Protein Intake and Appetite Regulation:
A high-protein diet induces sustained reductions in appetite:This research indicates that increasing dietary protein can lead to a sustained decrease in caloric intake, potentially aiding in weight loss. pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov
Estrogen Replacement and Muscle Strength:
Estrogen replacement and skeletal muscle: mechanisms and population health:This article discusses how estrogen therapy can enhance muscle strength and function beyond just increasing muscle mass. pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov
Ghrelin's Role in Appetite and Body Weight Regulation:
Ghrelin and the short- and long-term regulation of appetite and body weight:This study explores how ghrelin injections can stimulate food intake and influence feeding behaviors. pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov
Exercise and Estrogen Levels in Postmenopausal Women:
Effect of aerobic and anaerobic exercise on estrogen level, fat mass, and lean mass in postmenopausal women:This research highlights the effectiveness of exercise programs in improving estradiol levels and body composition in postmenopausal women. pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov
Ghrelin's Functions and Regulation:
Ghrelin – Physiological Functions and Regulation:This review provides insights into the wide range of functions ghrelin has, including its role in regulating food intake and energy metabolism. pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov