Is your body functioning properly? I think this is an important question to ask yourself.
A balanced meal provides all the essential nutrients your body needs to function properly. It typically includes a mix of macronutrients (carbohydrates, proteins, and fats) and micronutrients (vitamins and minerals). Women over 40 often face unique nutritional challenges, including the potential for inadequate protein intake.
Simply put, a lot of women over 40 don't get enough protein in their daily lives!
That's why I created a high-protein food list (Healthy Eating Guide) so you can print it out and stick it on your fridge! Click to go straight to the FREE Printable PDF.
What is Protein?
Protein is a vital nutrient that serves as the building blocks of our body.
It's essential for repairing tissues, building muscles, and maintaining a healthy immune system.
Proteins comprise smaller units called amino acids, which our bodies need to function properly. There are 20 different amino acids, and nine of them are considered essential because our bodies cannot produce them; we must get them from our diet.
How Much Protein Do You Need Per Day?
This question is kind of controversial!
Also, the amount of protein you need daily depends on your age, gender, and activity level.
These recommendations come from the International Society of Sports Nutrition (ISSN), so they’ll be relevant for most people who exercise.
The general rule to try is this:
- 0.64-0.91 grams of protein / lb / day (or 1.4-2 grams / kg)
- OR 30-40 grams of protein per meal to simplify things
Example: If you weigh 150 pounds and are active,
- 150 lbs×0.64 g/lb=96 grams of protein per day (lower end)
- 150 lbs×0.91 g/lb=136.5 grams of protein per day (upper end)
This helps maintain muscle mass, which is crucial as we age and our bodies naturally lose muscle.
Why is Protein Important?
Protein is crucial for several reasons:
- Muscle Mass: Helps build and maintain muscle mass, which is vital as we age. Muscle loss can lead to decreased strength and increased risk of falls and fractures.
- Weight Loss: High-protein foods help you feel fuller longer, aiding in weight loss by reducing overall calorie intake. Protein takes longer to digest compared to carbohydrates, which can help control appetite.
- Body Functions: Supports various bodily functions, including hormone production, enzyme function, and immune response. Proteins are involved in virtually every cellular process.
- Healthy Aging: Adequate protein intake supports healthy skin, hair, and nails, which can be affected by the aging process.
Benefits of Protein
- Weight Management: Helps control appetite and reduce overall calorie intake by making you feel fuller for longer periods. This can prevent overeating and snacking on unhealthy foods.
- Heart Health: Supports healthy cholesterol levels and reduces the risk of heart disease. Choosing lean protein sources over fatty cuts of meat can help maintain heart health.
- Blood Sugar Control: Stabilizes blood sugar levels, preventing spikes and crashes that can lead to cravings and overeating.
- Bone Health: Protein is essential for maintaining strong bones, especially when combined with calcium and vitamin D.
- Metabolism Boost: Protein has a higher thermic effect of food (TEF) compared to fats and carbohydrates, meaning it requires more energy to digest and can help boost your metabolism.
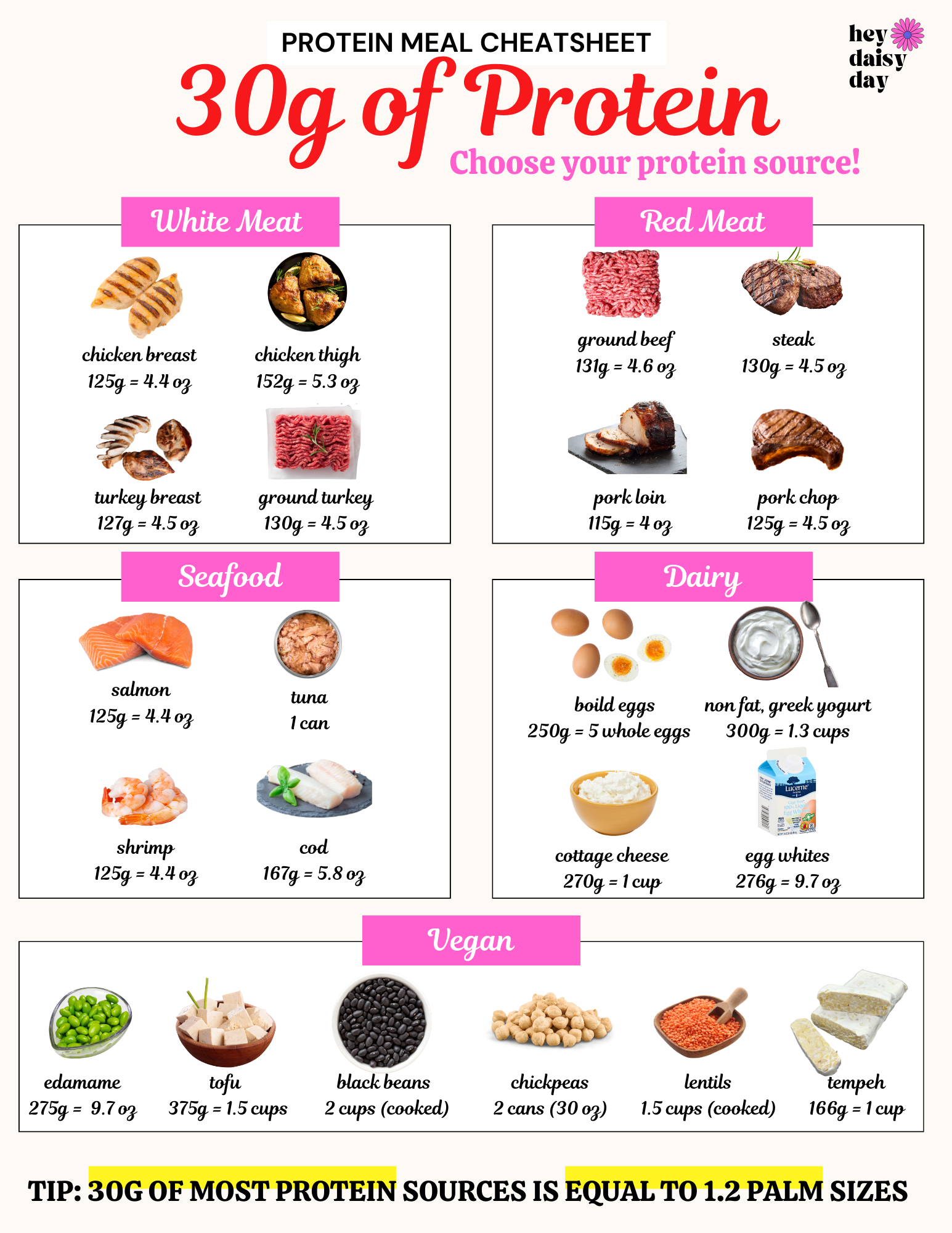
Top 10 High Protein Foods
- Egg Whites: Low in calories but packed with protein. One large egg white provides about 3.6 grams of protein and is almost fat-free, making it an excellent choice for those watching their calorie intake.
- Greek Yogurt: A delicious, creamy source of protein. A typical serving (1 cup) contains about 15-20 grams of protein, making it a great snack or breakfast option.
- Chicken Breast: Lean and versatile. A 4.5 oz serving provides about 31 grams of protein. It's also low in fat, making it a healthy option.
- Cottage Cheese: Rich in protein and calcium. One cup (270 grams) contains about 30 grams of protein. It's a great snack or addition to meals.
- Lean Pork Tenderloin: Low in fat, high in protein. A 100-gram serving provides about 22 grams of protein. It's a flavorful alternative to chicken and beef.
- Soy Products: Great for those following a plant-based diet. Tofu, tempeh, and edamame are excellent sources of protein. A 1.5 cups serving of tofu provides about 30 grams of protein.
- Fatty Fish: Like salmon, which also provides healthy fats. A 4.4 oz serving of salmon offers about 30 grams of protein, along with omega-3 fatty acids that support heart health.
- Beans and Legumes: Such as black beans, which are fiber-rich. One cup (172 grams) of black beans contains about 15 grams of protein and provides essential nutrients like iron and magnesium.
- Nuts and Seeds: Pumpkin seeds and almond butter are great protein sources. A quarter-cup (30 grams) of pumpkin seeds provides about 9 grams of protein.
- Lean Beef: Opt for cuts like sirloin or tenderloin for less fat. A 4.6 oz serving of lean beef provides about 30 grams of protein.
Tips to Eat More Protein
- Plan Your Meals: Include a source of protein in every meal. Aim for a mix of animal and plant-based proteins to ensure a balanced intake of nutrients.
- Snack Smart: Choose high-protein snacks like Greek yogurt, cottage cheese, or nuts. These can help keep you full between meals and prevent unhealthy snacking.
- Mix It Up: Combine plant-based and animal-based proteins for variety. For example, add beans to salads or mix tofu into stir-fries.
- Cook in Bulk: Prepare protein-rich foods in advance, so they're ready to eat. Cook large batches of chicken breast, lean beef, or tofu to use in various meals throughout the week.
- Read Labels: Check food labels for protein content to ensure you're getting enough. Many packaged foods now list protein content per serving.
What is Considered High Protein?
A food is generally considered high in protein if it contains more than 10 grams of protein per serving. Foods like lean meats, dairy products, and certain plant-based options can all be high-protein choices. It's also important to consider the overall quality of the protein, which includes the presence of essential amino acids.
Printable High-Protein Food List (included in Healthy Eating Guide)
To help you get started, here’s a free printable PDF chart with high-protein foods (included in Healthy Eating Guide) you can find at your local grocery store. This chart includes a variety of protein sources, from animal products to plant-based options, ensuring you have a diverse selection to choose from. [Download Now]
Understanding High-Protein Foods
Animal-Based Protein:
- Lean Meats: Chicken breast, turkey, lean beef, pork tenderloin, and game meats.
- Fish and Seafood: Salmon, tuna, shrimp, and other fatty fish.
- Dairy Products: Greek yogurt, cottage cheese, low-fat milk, and other low-fat dairy options.
- Eggs: Particularly egg whites, which are low in calories and high in protein.
Plant-Based Protein:
- Beans and Legumes: Black beans, chickpeas, lentils, and soy products like tofu and tempeh.
- Nuts and Seeds: Almonds, pumpkin seeds, chia seeds, and nut butters like peanut and almond butter.
- Whole Grains: Quinoa, farro, and other whole grains that provide a mix of protein and fiber.
- Vegetables: Certain vegetables like broccoli and Brussels sprouts have higher protein content compared to others.
Importance of Protein Quality
Not all proteins are created equal. The quality of protein depends on its amino acid profile. Complete proteins contain all nine essential amino acids. Animal-based proteins are usually complete, while most plant-based proteins are incomplete. However, by combining different plant-based sources, such as beans and rice, you can create a complete protein profile.
Balancing Protein with Other Nutrients
While protein is essential, it's important to maintain a balanced diet that includes a variety of nutrients. Incorporate healthy fats, such as those found in olive oil and fatty fish, and plenty of fruits and vegetables for fiber, vitamins, and minerals. Avoid overly processed foods and sugary drinks, which can contribute to weight gain and other health issues.
Incorporating high-protein foods into your diet can have numerous health benefits, especially for those over 40 and women looking to get in shape and lose weight.
Remember to balance your protein intake with other important nutrients and maintain a healthy, varied diet. For personalized advice, consult a healthcare provider or a registered dietitian.
This comprehensive guide provides you with the knowledge and tools to make informed decisions about your protein intake. Use the printable high-protein food list (30g per meal chart) as a great resource to help you navigate your protein needs at the grocery store and plan healthy, balanced meals that support your overall well-being.